
Prior to the MW sequence, the NV ensemble is initialized in | + ⟩ while once its state encodes the desired information it is optically read out in the σ y basis. The lowercase letter appears for long range couplings across the two halves of a symmetric system. The reason why we use Hertz, is because it's the same coupling constant no matter what NMR spectrometer you're using, so it doesn't matter what the operating.
#Inmr shifts and j couplings written out free#
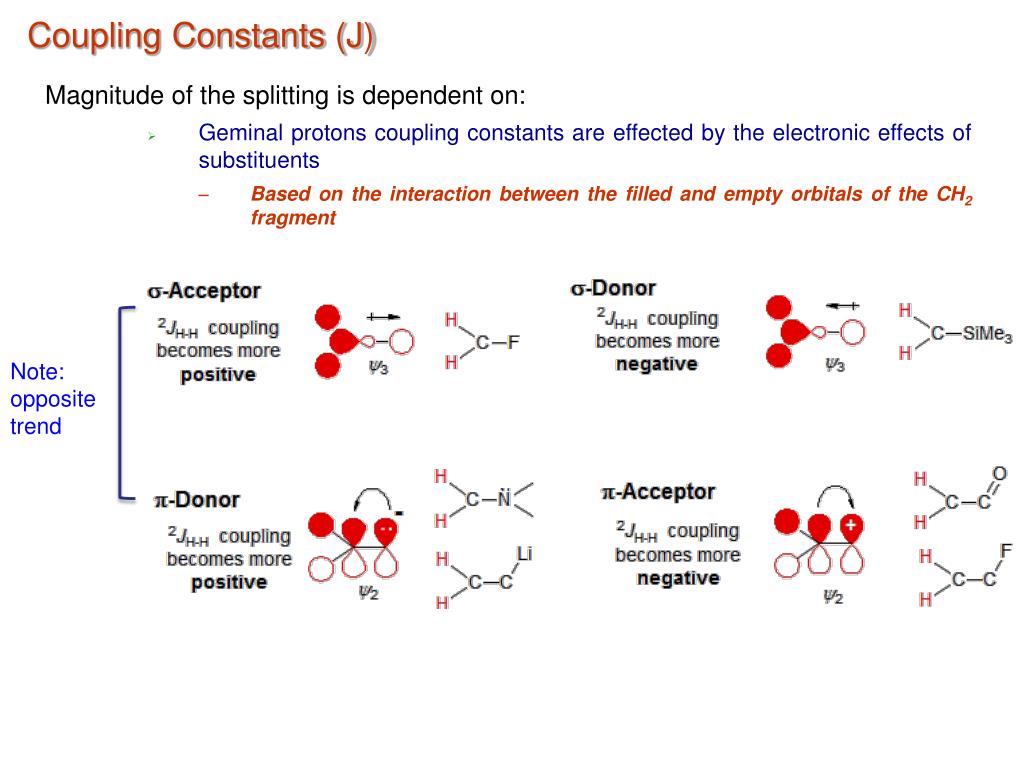
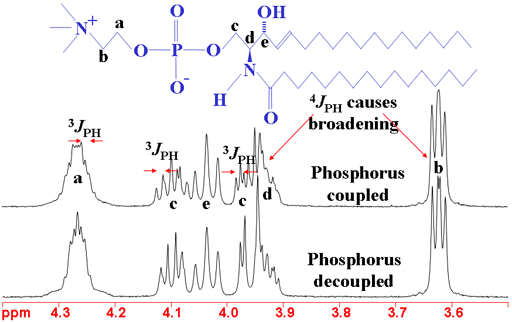
Note that the NVs remain inactive during the long free precession stages of the sample, providing our protocol with increased spectral resolution regardless of the sensor coherence time. The coupling constant is measured in Hertz, so it turns out to be 1.4 Hz, and if it's 1.4 Hz for this one, it must be 1.4 Hz for this one, because those protons are coupled together. A shift to the left suggests diastolic dysfunction (red). Using the information here above (see the paragraph. Third panel: MW pattern-in our case an X Y 4 sequence-on each NV devised to capture the induced signal. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. You can easily recognize couples of nuclei with identical chemical shifts and identical coupling constants. The coupling travels through electrons J is sensitive to molecular structure J decays as the of bonds separating spins A and X increases iii. The coupling constant J is independent of B 0 its value is expressed in Hz and not in ppm’s. The depicted case shows three B i fields as a consequence of the splitting among three magnetization vectors that spin at rates δ 1, δ 2, and δ 3. J/2 if spin A Features to notice about J-couplings i. and J represent chemical shifts and scalar coupling, respectively (in. When its time to specify the first J he is soon in trouble. Proton NMR chemical shifts and coupling constants for brain metabolites. One may therefore be tempted to put them into the same row. These have different amplitudes due to the distinct projections of each rotating M k ( t ) on the Z axis. TOCSY is used to average out the chemical shift interaction and create an average. Nuclei A and D have identical chemical shifts and identical coupling constants. (b) First panel: RF control sequence with interleaved free precessions. The direct dimension of selective J spectroscopy, however, is not suitable for the measurement of scalar coupling constants and can be further improved by pure-shift acquisition. The phase covered by each M k ( t )-this is ϕ k = δ k τ-is encoded in the amplitude of the oscillating field generated via controlled rotations of these vectors. The observed chemical shift for C is 27.1 ppm, indicating that the 11-methyl group is in the e/irfo-position.
For a time τ each magnetization vector M k ( t ) precesses according to the local field at the position of the nuclear spin. (a) An initial RF π / 2 pulse brings the sample thermal polarization to the orthogonal plane and triggers the AERIS protocol consisting of free precessions and induced rotation stages. Smaller shifts of either sign can occur further out.
I understand that the strong delocalisation in the aromatic ring may tend to "even out" the electron distribution across all the aromatic $\ce $.Custom signal production and measurement. The Calculation of Indirect Nuclear SpinSpin Coupling Constants 102. This point of convergence is called the J Manager. Clearly, the aromatic protons are in different chemical environments due to the fact that they are different distances away from the substituents from the benzene ring. iNMR gives you many tools to derive the most common NMR parameters (chemical shifts and coupling constants) and a single tool where everything converges upon. Recently, I have started to learn about nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) in school and something which I cannot seem to reconcile is the fact that all aromatic protons on any substituted benzene ring would give the same chemical shift.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
